Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells. This condition can be classified into two main types: alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is linked to excessive alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which occurs in individuals who drink little to no alcohol. As you delve deeper into this topic, you will discover that fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly prevalent, affecting millions of people worldwide.
It often goes unnoticed, as many individuals may not experience any symptoms in the early stages. The liver plays a crucial role in your body, responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and storing nutrients. When fat builds up in the liver, it can lead to inflammation and damage, potentially resulting in more severe liver conditions such as steatohepatitis, fibrosis, or cirrhosis.
Understanding the implications of fatty liver disease is essential for recognizing its potential impact on your overall health and well-being. By being informed about this condition, you can take proactive steps to manage or even reverse its effects.
Key Takeaways
- Fatty liver disease is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and potential liver damage.
- Causes and risk factors for fatty liver disease include obesity, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Symptoms of fatty liver disease may not be noticeable, but can include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and jaundice. Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests and imaging studies.
- Early intervention is crucial in preventing the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis and liver failure.
- Reversing fatty liver through diet and exercise is possible, with a focus on weight loss, healthy eating, and regular physical activity.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, and understanding these causes can help you identify your own risk. One of the primary culprits is obesity, as excess body weight can lead to increased fat accumulation in the liver. If you find yourself struggling with weight management, it’s essential to recognize that this could be a significant risk factor for developing fatty liver disease.
Additionally, metabolic disorders such as diabetes and high cholesterol levels can also increase your likelihood of developing this condition. Other risk factors include a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, and certain medications.
Furthermore, certain medications, such as corticosteroids and some cancer treatments, can contribute to fat buildup in the liver. By being aware of these risk factors, you can take steps to mitigate them and protect your liver health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Fatty liver disease often presents with few or no symptoms in its early stages, making it challenging to diagnose without proper medical evaluation. However, as the condition progresses, you may begin to experience symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or an enlarged liver. If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
They may recommend blood tests to assess liver function or imaging studies like ultrasound or CT scans to visualize fat accumulation in the liver. Diagnosis is essential for determining the severity of the condition and guiding appropriate treatment options. If you suspect that you may have fatty liver disease, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice.
Early detection can significantly improve your chances of reversing the condition and preventing further complications.
The Importance of Early Intervention
| Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Improved developmental outcomes | 80% of children show improvement with early intervention |
| Reduced special education needs | 50% reduction in the need for special education services |
| Cost savings | Every 1 invested in early intervention saves 7 in future costs |
| Increased school readiness | Children who receive early intervention are more prepared for school |
Early intervention is critical when it comes to managing fatty liver disease. The earlier you recognize the condition and take action, the better your chances are of reversing its effects and preventing progression to more severe liver diseases. If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to serious complications such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
By prioritizing early intervention, you can safeguard your liver health and enhance your overall quality of life. Taking proactive steps early on can also help you avoid the emotional and physical toll that comes with advanced liver disease. You may find that making lifestyle changes now not only benefits your liver but also improves your overall health and well-being.
Whether it’s adopting a healthier diet or increasing your physical activity levels, early intervention empowers you to take control of your health journey.
Reversing Fatty Liver through Diet and Exercise
One of the most effective ways to reverse fatty liver disease is through dietary changes and regular exercise. If you’re looking to improve your liver health, consider adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing your intake of processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats can significantly impact fat accumulation in the liver.
You might also want to consider incorporating foods known for their liver-supportive properties, such as leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish. In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity is crucial for reversing fatty liver disease. Engaging in aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, or cycling can help you burn excess fat and improve insulin sensitivity.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. By combining a healthy diet with regular exercise, you can create a powerful strategy for reversing fatty liver disease and enhancing your overall health.
Medications and Medical Treatments
While lifestyle changes are often the first line of defense against fatty liver disease, there are also medications and medical treatments available for those who may need additional support. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications aimed at managing underlying conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol that contribute to fatty liver disease. These medications can help improve your overall metabolic health and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
In some cases, more advanced treatments may be necessary if lifestyle changes alone are insufficient. For instance, if you have developed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and damage to liver cells, your doctor may recommend specific therapies aimed at reducing inflammation and promoting liver health. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action tailored to your individual needs.
Potential Complications of Untreated Fatty Liver
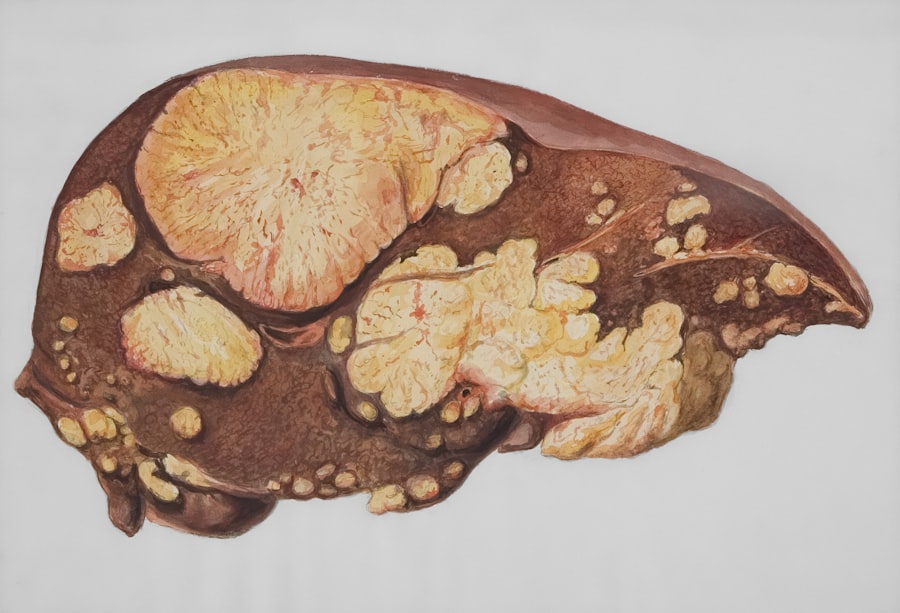
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to several serious complications that can significantly impact your health. One of the most concerning outcomes is the progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and damage to liver cells. This condition can further progress to fibrosis (scarring of the liver) and eventually cirrhosis, which is characterized by severe scarring that impairs liver function.
Cirrhosis can lead to life-threatening complications such as liver failure or hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). Additionally, individuals with cirrhosis may experience portal hypertension, which can cause varices (enlarged veins) that are prone to bleeding. Understanding these potential complications underscores the importance of addressing fatty liver disease early on.
By taking proactive measures now, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing these severe health issues.
Reversing Fatty Liver: Is it Possible?
The good news is that reversing fatty liver disease is indeed possible with the right approach. Many individuals have successfully improved their liver health through lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. Research has shown that even modest weight loss—around 5-10% of your body weight—can lead to significant improvements in liver fat content and overall function.
It’s important to remember that reversing fatty liver disease is not an overnight process; it requires commitment and consistency over time. However, with determination and the right support system in place, you can achieve lasting results that benefit not only your liver but also your overall health.
Reversing Fatty Liver: How to Get Started
If you’re ready to take action toward reversing fatty liver disease, start by assessing your current lifestyle habits. Take note of your dietary choices and physical activity levels; this self-awareness will help you identify areas for improvement. Begin by setting realistic goals for yourself—whether it’s incorporating more fruits and vegetables into your meals or committing to regular exercise sessions each week.
Consider seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist who specializes in liver health; they can provide personalized recommendations tailored to your needs. Additionally, surrounding yourself with a supportive community—whether it’s friends or family—can help keep you motivated on your journey toward better health.
Success Stories: Reversing Fatty Liver
Many individuals have successfully reversed their fatty liver disease through dedication and lifestyle changes. These success stories serve as powerful reminders that transformation is possible with commitment and effort. For instance, one individual shared their journey of losing weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise; they reported feeling more energetic and experiencing improved lab results after just a few months.
Another success story highlights how a person diagnosed with NASH was able to reverse their condition by making significant dietary changes and incorporating physical activity into their daily routine. Their determination not only improved their liver health but also enhanced their overall quality of life. These stories illustrate that with perseverance and the right strategies in place, reversing fatty liver disease is achievable.
Seeking Professional Help for Reversing Fatty Liver
As you embark on your journey toward reversing fatty liver disease, seeking professional help can be invaluable. A healthcare provider specializing in liver health can offer guidance tailored specifically to your needs. They can help monitor your progress through regular check-ups and lab tests while providing support along the way.
Additionally, consider working with a registered dietitian who can assist you in creating a personalized meal plan that aligns with your goals for improving liver health. Remember that you don’t have to navigate this journey alone; reaching out for professional support can empower you to make lasting changes that benefit both your liver and overall well-being.
Fatty liver disease is a growing concern for many individuals, especially as lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise play a significant role in its development and progression. While some may wonder if it’s too late to reverse fatty liver, there are steps that can be taken to improve liver health and potentially reverse the condition. For those interested in learning more about managing and reversing fatty liver disease, a related article on this topic can be found on Explore Senior Health. This resource provides valuable insights and practical advice for those looking to make positive changes. You can read more about it by visiting this article.
WATCH THIS! 🧃The 60-Year Liver Lie: Why Your “Healthy” Juice Is Destroying Your Liver
FAQs
What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and potential damage to the liver cells.
What are the causes of fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease can be caused by excessive alcohol consumption (alcoholic fatty liver disease) or by non-alcoholic factors such as obesity, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and rapid weight loss.
Is it too late to reverse fatty liver?
It is not necessarily too late to reverse fatty liver disease, especially in the early stages. Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss can help improve the condition of the liver.
What are the potential complications of fatty liver disease?
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
How can fatty liver disease be diagnosed?
Fatty liver disease can be diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes a liver biopsy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for fatty liver disease?
Treatment for fatty liver disease involves lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol.
