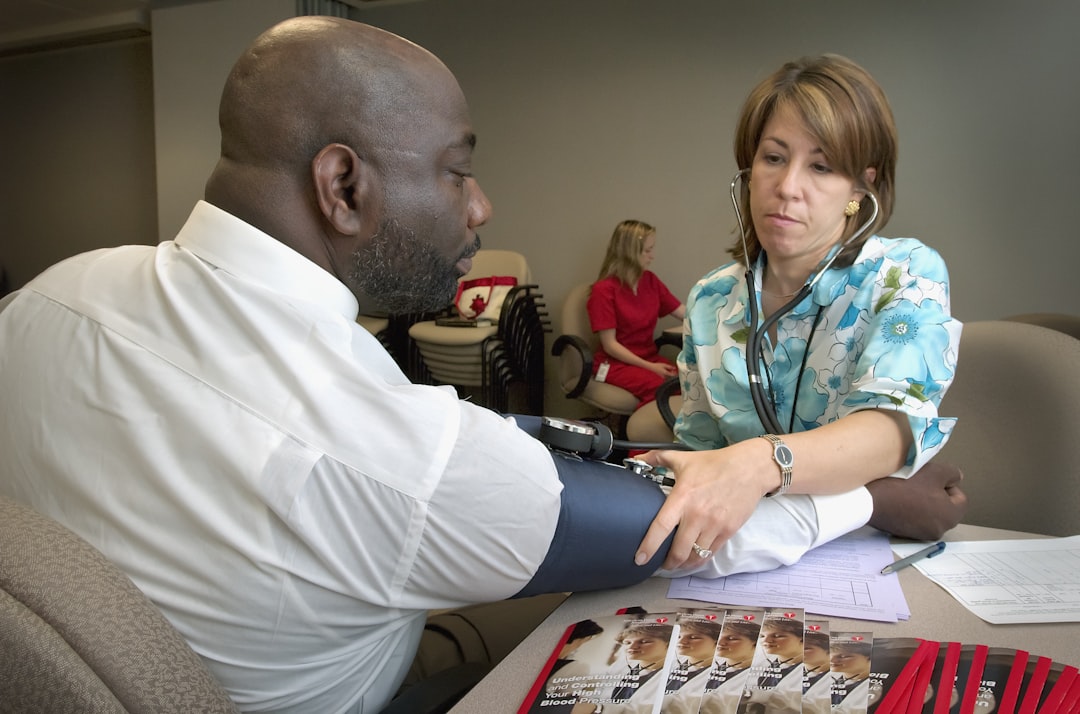
Blood pressure is a critical indicator of your cardiovascular health, reflecting the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of your arteries. It is expressed in two numbers: systolic and diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure, the first number, measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while the diastolic pressure, the second number, gauges the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
For instance, a reading of 120/80 mmHg is considered normal, with 120 representing the systolic pressure and 80 the diastolic pressure. Understanding these numbers is essential for recognizing your health status and making informed decisions about your lifestyle and medical care. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
Conversely, low blood pressure can also pose risks, such as dizziness and fainting. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain your blood pressure within a healthy range. Regular monitoring allows you to track changes over time and identify potential issues early on.
By understanding what blood pressure is and how it functions, you empower yourself to take control of your health and make proactive choices that can lead to a longer, healthier life.
Key Takeaways
- Regular home monitoring helps detect and manage blood pressure effectively.
- Selecting an accurate and user-friendly blood pressure monitor is crucial.
- Proper preparation and technique ensure reliable blood pressure readings.
- Tracking and interpreting results aids in understanding health trends.
- Seek medical advice if readings are consistently abnormal or symptoms arise.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Pressure at Home
Monitoring your blood pressure at home is an essential practice that can significantly enhance your health management. It provides you with immediate feedback on how your lifestyle choices—such as diet, exercise, and stress management—affect your cardiovascular health. By regularly checking your blood pressure, you can identify trends and fluctuations that may require attention.
This proactive approach allows you to make timely adjustments to your lifestyle or medication regimen, ultimately reducing the risk of severe health issues. Moreover, home monitoring can help you become more engaged in your health care. When you take responsibility for tracking your blood pressure, you develop a deeper understanding of your body and its responses to various factors.
This knowledge can foster better communication with your healthcare provider, as you can share accurate data during appointments. Additionally, having a record of your readings can help your doctor make more informed decisions regarding treatment options or lifestyle recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
Choosing the Right Blood Pressure Monitor

Selecting the appropriate blood pressure monitor is crucial for obtaining accurate readings. There are various types available on the market, including manual monitors that require a stethoscope and automatic digital monitors that provide readings at the push of a button. For most individuals, an automatic digital monitor is recommended due to its ease of use and convenience.
When choosing a monitor, consider factors such as accuracy, cuff size, and additional features like memory storage or Bluetooth connectivity for tracking data on your smartphone. It’s also essential to ensure that the monitor you select is validated for accuracy by reputable organizations.
Additionally, consider whether the monitor fits comfortably on your arm or wrist; an ill-fitting cuff can lead to inaccurate readings. By investing time in selecting the right blood pressure monitor, you set yourself up for success in managing your health effectively.
Preparing to Measure Blood Pressure
Preparation is key to obtaining accurate blood pressure measurements. Before taking a reading, it’s important to create an environment conducive to accurate results. Find a quiet space where you can sit comfortably without distractions.
This routine helps account for daily fluctuations caused by various factors such as activity levels or stress. Additionally, ensure that you are in a relaxed state before taking your measurement.
Sit quietly for at least five minutes before using the monitor; this allows your heart rate and blood pressure to stabilize. Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals for at least 30 minutes prior to measuring your blood pressure, as these can temporarily elevate your readings. By taking these preparatory steps seriously, you enhance the reliability of your measurements and gain a clearer picture of your cardiovascular health.
Taking the Blood Pressure Measurement
| Step | Action | Details / Tips | Metric / Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare Yourself | Rest for 5 minutes before measuring; avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking 30 minutes prior | Rest time: 5 minutes |
| 2 | Position Yourself Correctly | Sit with back supported, feet flat on the floor, arm supported at heart level | Arm height: Heart level |
| 3 | Apply the Cuff Properly | Place cuff on bare upper arm, about 1 inch above elbow crease; ensure snug fit | Cuff placement: 1 inch above elbow |
| 4 | Take Multiple Readings | Take 2-3 readings, 1 minute apart; record all results | Number of readings: 2-3 |
| 5 | Record the Results | Note systolic and diastolic pressures along with date and time | Example: 120/80 mmHg |
| 6 | Use Validated Equipment | Use an automatic, clinically validated blood pressure monitor | Device type: Automatic, validated |
| 7 | Measure at Consistent Times | Measure blood pressure at the same times daily, preferably morning and evening | Measurement times: Morning & Evening |
When you’re ready to take your blood pressure measurement, follow the instructions provided with your monitor carefully. Position yourself comfortably in a chair with your back supported and feet flat on the floor. Rest your arm on a table at heart level with the palm facing upward.
If you’re using a cuff-style monitor, wrap the cuff snugly around your upper arm or wrist according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Ensure that there is enough space between the cuff and your skin for comfort but not so much that it affects the reading. Once everything is set up correctly, activate the monitor and allow it to inflate automatically if it’s an automatic device.
Remain still and quiet during the measurement process; movement or talking can lead to inaccurate results. After the reading is complete, take note of both the systolic and diastolic numbers displayed on the screen. If you’re using a manual monitor, listen carefully for the sounds through the stethoscope as you deflate the cuff to determine your blood pressure accurately.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting your blood pressure readings is essential for understanding your cardiovascular health status. A normal reading typically falls below 120/80 mmHg. If your systolic number is between 120-129 and your diastolic number is below 80, you may be classified as having elevated blood pressure.
Hypertension is generally diagnosed when readings consistently exceed 130/80 mmHg. It’s important to remember that one high reading does not necessarily indicate hypertension; multiple readings over time are needed for an accurate assessment. If you find that your readings are consistently high or low, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
They can help determine whether lifestyle changes or medication may be necessary to manage your blood pressure effectively. Understanding how to interpret these numbers empowers you to take charge of your health and seek appropriate interventions when needed.
Recording and Tracking Blood Pressure Readings
Keeping a record of your blood pressure readings is vital for monitoring trends over time and sharing information with healthcare providers. You can use a simple notebook or digital tools like apps designed for tracking health metrics. When recording your readings, include the date and time of each measurement along with any relevant notes about factors that may have influenced the reading—such as stress levels or recent physical activity.
Tracking these readings allows you to identify patterns that may emerge over weeks or months. For instance, if you notice that your blood pressure tends to rise during stressful periods or after consuming certain foods, this information can guide you in making lifestyle adjustments. Additionally, having a comprehensive record of your measurements can facilitate more productive discussions with your healthcare provider during appointments.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure Measurements
Several factors can influence blood pressure measurements, making it essential to be aware of them when monitoring at home. Physical activity is one significant factor; engaging in exercise can temporarily elevate blood pressure levels due to increased heart rate and circulation demands. Conversely, resting or relaxing can lead to lower readings.
Emotional states such as stress or anxiety can also impact measurements; elevated stress hormones can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure. Other factors include dietary choices—particularly sodium intake—and hydration levels. Consuming high-sodium foods can lead to increased blood volume and higher blood pressure readings.
Additionally, dehydration can cause fluctuations in blood pressure as well. Medications may also play a role; certain drugs can either raise or lower blood pressure depending on their effects on the cardiovascular system. Being mindful of these factors helps ensure that you interpret your readings accurately and understand their context.
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Monitoring
To achieve accurate blood pressure measurements consistently, consider implementing several best practices into your routine. First and foremost, always use the same arm for measurements; this consistency helps eliminate variability in readings caused by differences between arms. Additionally, ensure that you are using a properly calibrated monitor; check its accuracy periodically against a professional device if possible.
Timing is also crucial; try to measure your blood pressure at similar times each day—preferably when you are relaxed and not under stress. Avoid measuring immediately after physical activity or during times of emotional distress for more reliable results. Lastly, take multiple readings during each session—two or three measurements spaced about one minute apart—and average them for a more accurate representation of your blood pressure.
When to Seek Medical Help
Knowing when to seek medical help regarding blood pressure concerns is vital for maintaining good health. If you consistently record high readings—especially those exceeding 130/80 mmHg—it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance on managing hypertension effectively. Additionally, if you experience symptoms such as severe headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain alongside high blood pressure readings, seek immediate medical attention.
Conversely, if you notice unusually low readings—especially those below 90/60 mmHg—accompanied by symptoms like fainting or extreme fatigue, it’s important to reach out to a healthcare provider as well. Understanding when to seek help ensures that you receive timely interventions that can prevent complications related to both high and low blood pressure.
Benefits of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regularly monitoring your blood pressure offers numerous benefits that extend beyond simply keeping track of numbers. One significant advantage is early detection; by identifying changes in your blood pressure over time, you can catch potential issues before they escalate into serious health problems like heart disease or stroke. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions that can significantly improve outcomes.
Moreover, consistent monitoring fosters greater awareness of how lifestyle choices impact your cardiovascular health. As you track changes in response to diet modifications or exercise routines, you gain valuable insights into what works best for you personally. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about maintaining a healthy lifestyle while also enhancing communication with healthcare providers regarding treatment options tailored specifically to your needs.
In conclusion, understanding and monitoring blood pressure is an essential aspect of maintaining overall health and well-being. By taking proactive steps in measuring and interpreting these readings at home, you empower yourself to make informed decisions about lifestyle changes and medical care while fostering better communication with healthcare professionals.
To ensure accurate readings when measuring blood pressure at home, it’s essential to follow proper techniques and guidelines. For more detailed information on this topic, you can refer to the article on senior health, which provides valuable insights and tips. Check it out here: How to Measure Blood Pressure Correctly at Home.
FAQs
What is the best time to measure blood pressure at home?
The best times to measure blood pressure at home are typically in the morning before taking any medications and in the evening before dinner. It is important to take measurements at the same times each day for consistency.
How should I prepare before measuring my blood pressure?
Before measuring your blood pressure, sit quietly for at least 5 minutes, avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking for at least 30 minutes prior. Ensure you are relaxed and seated with your back supported and feet flat on the floor.
What is the correct position for measuring blood pressure?
Sit upright with your back supported, feet flat on the floor, and legs uncrossed. Rest your arm on a flat surface at heart level, with the cuff placed on bare skin around the upper arm.
How do I choose the right blood pressure monitor for home use?
Select an automatic, cuff-style monitor that fits your arm size properly. Upper arm monitors are generally more accurate than wrist or finger devices. Look for monitors validated by recognized health organizations.
How often should I measure my blood pressure at home?
For monitoring purposes, it is recommended to take two readings, one minute apart, twice daily (morning and evening) for several days. Follow your healthcare provider’s advice on frequency.
What should I do if my blood pressure readings are consistently high or low?
If your readings are consistently outside the normal range, contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Do not adjust or stop medications without professional advice.
Can I use a wrist blood pressure monitor instead of an upper arm monitor?
While wrist monitors can be convenient, they are generally less accurate and more sensitive to body position. If using a wrist monitor, follow instructions carefully and keep the wrist at heart level during measurement.
Why is it important to measure blood pressure correctly at home?
Accurate home blood pressure measurements help monitor your health, guide treatment decisions, and detect potential problems early. Incorrect technique can lead to misleading readings and inappropriate management.
Should I record my blood pressure readings?
Yes, keeping a log of your readings with date and time helps track trends and provides valuable information for your healthcare provider during consultations.
Can stress or talking affect blood pressure readings?
Yes, stress, talking, or moving during measurement can temporarily raise blood pressure. It is important to remain still and silent while taking readings for accurate results.
