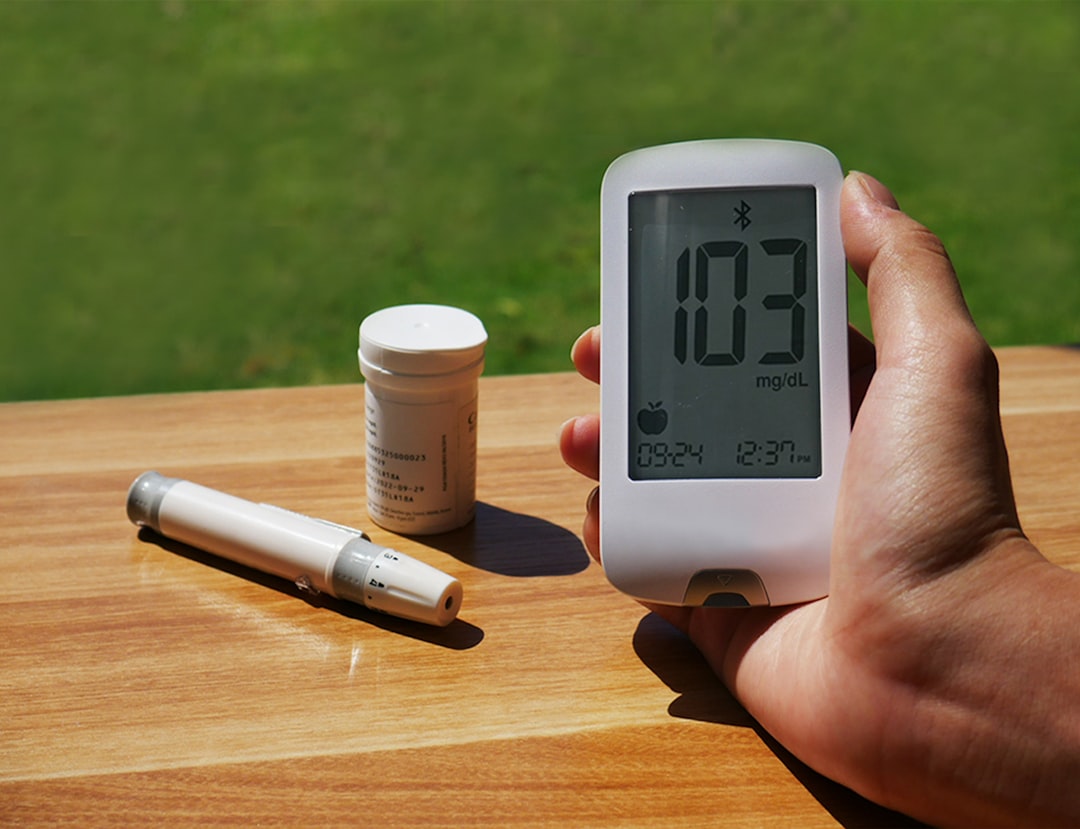
Blood pressure management is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Hypertension affects approximately 45% of adults in the United States and becomes increasingly prevalent with age.
Drug interactions occur when one medication affects the absorption, metabolism, distribution, or elimination of another drug. These interactions can result in decreased efficacy of blood pressure medications, increased risk of hypotension, or enhanced side effects. The likelihood of clinically significant drug interactions increases with the number of medications taken concurrently, a situation known as polypharmacy.
Older adults face particular risks due to age-related changes in drug metabolism and the higher prevalence of multiple chronic conditions requiring pharmaceutical management. Studies indicate that adults over 65 take an average of four to five prescription medications daily, substantially increasing the potential for drug interactions. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate medication regimens and monitor patients for signs of interactions to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing risks.
Key Takeaways
- Managing blood pressure medication interactions is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness, especially in older adults.
- Common blood pressure drugs can interact with other medications, increasing risks of side effects or reduced efficacy.
- Older adults face higher risks due to multiple medications, age-related changes, and existing health conditions.
- Healthcare providers play a key role in monitoring, adjusting medications, and educating patients about potential interactions.
- Regular communication, lifestyle changes, and medication reviews help prevent interactions and support optimal blood pressure control.
Common Blood Pressure Medications and Their Potential Interactions
There are several classes of medications commonly prescribed to manage blood pressure, including diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers. Each of these medications works differently in the body and can interact with other drugs you may be taking. For instance, diuretics can lead to electrolyte imbalances when combined with certain supplements or medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
This can result in increased blood pressure rather than the desired decrease. ACE inhibitors, on the other hand, may interact with potassium supplements or certain diuretics, leading to dangerously high potassium levels in your blood. Beta-blockers can also have interactions with medications used for diabetes management, potentially masking symptoms of low blood sugar.
Understanding these potential interactions is vital for you to avoid complications and ensure that your blood pressure remains under control.
Identifying Risk Factors for Medication Interactions in Older Adults
As you age, your body undergoes various changes that can affect how medications are metabolized. Factors such as decreased kidney function, changes in liver metabolism, and alterations in body composition can all contribute to an increased risk of medication interactions. Additionally, older adults often take multiple medications for various health conditions, which further complicates the landscape of drug interactions.
Cognitive decline can also play a role in medication management. If you or a loved one struggles with memory issues, it may be challenging to keep track of all prescribed medications and their dosages. This can lead to unintentional overdosing or missing doses altogether, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
Being aware of these risk factors allows you to take proactive steps in managing your medication regimen effectively.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Managing Blood Pressure Med Interactions
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in managing blood pressure medication interactions. They are responsible for prescribing the right medications while considering your unique health profile and any other medications you may be taking. Regular communication with your healthcare provider is essential for ensuring that your treatment plan remains effective and safe.
Your healthcare provider should conduct thorough medication reviews during appointments, assessing not only the effectiveness of your current regimen but also any potential interactions with new prescriptions or over-the-counter medications.
Strategies for Preventing Medication Interactions in Older Adults
| Medication | Common Interaction | Effect on Blood Pressure | Risk Level | Notes for Older Adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors (e.g., Lisinopril) | Potassium-sparing diuretics | Increased potassium levels, risk of hyperkalemia | High | Monitor potassium levels regularly; risk of kidney impairment |
| Beta-blockers (e.g., Metoprolol) | Calcium channel blockers (e.g., Verapamil) | Excessive lowering of heart rate and blood pressure | Moderate | Monitor heart rate and blood pressure closely |
| Diuretics (e.g., Hydrochlorothiazide) | NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen) | Reduced diuretic efficacy, increased blood pressure | Moderate | Use NSAIDs cautiously; monitor blood pressure |
| Calcium Channel Blockers (e.g., Amlodipine) | Grapefruit juice | Increased drug concentration, risk of hypotension | Moderate | Avoid grapefruit juice to prevent toxicity |
| Alpha-blockers (e.g., Doxazosin) | Other antihypertensives | Enhanced blood pressure lowering effect | High | Risk of orthostatic hypotension; monitor for dizziness |
Preventing medication interactions requires a proactive approach on your part. One effective strategy is to maintain an up-to-date list of all medications you are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements. This list should be shared with every healthcare provider you see to ensure they have a complete picture of your medication regimen.
Another important strategy is to use a single pharmacy for all your prescriptions whenever possible. Pharmacists are trained to identify potential drug interactions and can alert you and your healthcare provider if they notice any concerns. Additionally, consider using pill organizers or medication management apps to help you keep track of dosages and schedules.
These tools can significantly reduce the likelihood of missed doses or accidental overdoses.
Monitoring and Adjusting Blood Pressure Medications in Older Adults
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is essential for older adults taking medication for hypertension. Your healthcare provider may recommend routine check-ups to assess how well your current regimen is working and whether any adjustments are necessary. This ongoing evaluation allows for timely modifications to your treatment plan based on your individual response to the medications.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may need to adjust dosages or switch medications altogether if interactions or side effects arise. Being open about any symptoms or concerns you experience can help facilitate these adjustments. Remember that managing blood pressure is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it requires continuous assessment and fine-tuning to achieve optimal results.
Communicating with Healthcare Providers About Medication Interactions
Effective communication with your healthcare providers is key to managing blood pressure medication interactions successfully. Be sure to discuss any new symptoms or side effects you experience while on medication. This information is crucial for your provider to make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions about potential interactions between your current medications and any new prescriptions or over-the-counter drugs you may be considering. Your healthcare provider should be willing to explain how different medications work together and what precautions you should take. By fostering an open dialogue, you can ensure that you are well-informed about your treatment options and any associated risks.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Blood Pressure Medication Management
In addition to medication management, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in controlling blood pressure. You can adopt several healthy habits that complement your treatment plan and enhance its effectiveness. For instance, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower blood pressure naturally.
Regular physical activity is another essential component of blood pressure management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. These lifestyle changes not only support your medication regimen but also contribute to overall well-being and quality of life.
Recognizing and Managing Side Effects of Blood Pressure Medications
Being aware of potential side effects from blood pressure medications is crucial for effective management. Common side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, or gastrointestinal issues. If you experience any adverse effects, it’s important to communicate these with your healthcare provider promptly.
In some cases, side effects may diminish over time as your body adjusts to the medication. However, if they persist or become bothersome, your healthcare provider may need to explore alternative treatment options or adjust dosages. Recognizing that side effects are a possibility allows you to approach your treatment with a proactive mindset.
The Importance of Regular Medication Reviews for Older Adults
Regular medication reviews are vital for older adults managing blood pressure and other chronic conditions. These reviews provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of current medications while identifying any potential interactions or side effects that may have arisen since the last appointment. During these reviews, it’s essential for you to be prepared with questions and concerns regarding your treatment plan.
Keeping an updated list of all medications and their dosages will facilitate a more productive discussion with your healthcare provider. By prioritizing regular medication reviews, you can ensure that your treatment remains aligned with your health goals.
Seeking Support and Resources for Managing Blood Pressure Med Interactions in Older Adults
Managing blood pressure medication interactions can be complex, but numerous resources are available to support you in this journey. Consider reaching out to local support groups or online communities where you can connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and strategies can provide valuable insights into managing your condition effectively.
Additionally, educational resources from reputable organizations can offer guidance on understanding blood pressure management and medication interactions. Your healthcare provider may also recommend specific resources tailored to your needs. By seeking support and utilizing available resources, you can enhance your ability to manage blood pressure effectively while minimizing the risk of medication interactions.
Managing blood pressure in older adults can be particularly challenging due to the potential interactions between various medications. A related article that delves into this topic can be found on Explore Senior Health, which discusses the importance of monitoring medication interactions to ensure safe and effective treatment. For more information, you can read the article [here](https://www.exploreseniorhealth.com/).
FAQs
What are common blood pressure medications prescribed to older adults?
Common blood pressure medications for older adults include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, and beta-blockers. These medications help manage hypertension and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Why are medication interactions a concern for older adults taking blood pressure drugs?
Older adults often take multiple medications for various health conditions, increasing the risk of drug interactions. These interactions can alter the effectiveness of blood pressure medications or cause adverse effects, making careful management essential.
Which types of medications commonly interact with blood pressure drugs in older adults?
Medications that commonly interact with blood pressure drugs include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), certain antidepressants, other antihypertensives, diuretics, and some over-the-counter supplements. These interactions can affect blood pressure control or increase side effects.
How can blood pressure medication interactions affect older adults?
Interactions can lead to increased blood pressure, dangerously low blood pressure, electrolyte imbalances, kidney problems, or other side effects. These effects can increase the risk of falls, hospitalization, or worsening of existing health conditions.
What steps can older adults take to minimize the risk of blood pressure medication interactions?
Older adults should maintain an up-to-date list of all medications and supplements, communicate regularly with healthcare providers, avoid self-medicating with over-the-counter drugs without consultation, and have their medications reviewed periodically for potential interactions.
Can lifestyle changes reduce the need for multiple blood pressure medications in older adults?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight management, limiting alcohol intake, and reducing sodium consumption can help control blood pressure and may reduce the need for multiple medications.
Should older adults consult their healthcare provider before stopping or changing blood pressure medications?
Absolutely. Older adults should never stop or adjust their blood pressure medications without consulting their healthcare provider, as abrupt changes can lead to serious health risks.
Are there specific monitoring recommendations for older adults on blood pressure medications?
Yes, regular monitoring of blood pressure, kidney function, and electrolyte levels is recommended to detect any adverse effects or interactions early and to ensure optimal medication effectiveness.
