Blood pressure management becomes increasingly important with advancing age, as hypertension affects a significant portion of the older adult population globally. Hypertension is commonly called a “silent killer” because it frequently develops without noticeable symptoms until serious health complications arise. The aging process naturally causes blood vessels to lose elasticity and become stiffer, while the heart may require increased effort to circulate blood effectively, resulting in elevated blood pressure risk.
Hypertension extends beyond elevated readings and can substantially affect overall health outcomes.
Regular blood pressure monitoring and appropriate management strategies are essential components of preventive healthcare for older adults.
Understanding these health risks enables individuals to make evidence-based decisions regarding their medical care and implement necessary lifestyle modifications or treatments to maintain optimal health.
Key Takeaways
- High blood pressure is a critical health issue among seniors, requiring careful understanding and management.
- Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, are essential for controlling senior hypertension.
- Medication adherence and proper management play a vital role in preventing complications from high blood pressure in seniors.
- Stress reduction techniques can significantly benefit seniors in managing their blood pressure levels.
- Ongoing medical check-ups and access to support resources are crucial for effective long-term blood pressure control in seniors.
Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure in Seniors
As you delve deeper into the factors contributing to high blood pressure, it’s crucial to recognize that age is just one piece of the puzzle. Various risk factors can elevate your chances of developing hypertension as you grow older. For instance, genetics plays a significant role; if your family has a history of high blood pressure, you may be more susceptible.
Additionally, lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and stress management can either mitigate or exacerbate these risks. Understanding these factors allows you to take control of your health proactively. Another critical aspect to consider is the impact of chronic conditions on your blood pressure.
Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and kidney disease can significantly increase your risk of hypertension. As you age, the likelihood of developing these conditions also rises, creating a compounded effect on your cardiovascular health. By being aware of these risk factors, you can work with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive plan tailored to your unique needs, ultimately reducing your risk of high blood pressure and its associated complications.
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring in Seniors
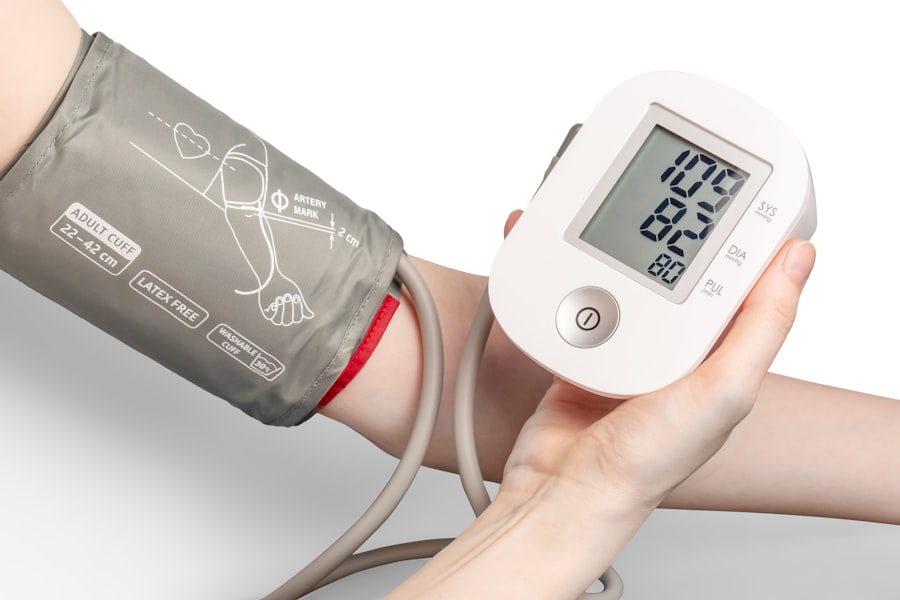
Regular blood pressure monitoring is an essential practice for seniors like yourself who wish to maintain optimal health. By keeping track of your blood pressure readings, you can identify trends and fluctuations that may require medical attention. This proactive approach allows you to catch potential issues early on, enabling timely interventions that can prevent more severe complications down the line.
Whether you choose to monitor your blood pressure at home or during routine doctor visits, consistency is key. Moreover, regular monitoring provides valuable data that can inform your healthcare provider’s decisions regarding treatment options. If you notice elevated readings over time, it may prompt discussions about lifestyle changes or medication adjustments.
This collaborative approach between you and your healthcare team fosters a sense of empowerment and control over your health journey. By prioritizing regular blood pressure monitoring, you take an active role in managing your well-being and reducing the risks associated with hypertension.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing High Blood Pressure in Seniors
Making lifestyle changes can be one of the most effective ways for you to manage high blood pressure. Small adjustments in your daily routine can lead to significant improvements in your overall health. For instance, incorporating more fruits and vegetables into your diet can provide essential nutrients while helping to lower blood pressure levels.
Additionally, reducing sodium intake is crucial; many processed foods contain high levels of salt that can contribute to hypertension. By being mindful of what you eat, you can create a heart-healthy diet that supports your well-being. Physical activity is another vital component in managing high blood pressure.
Engaging in regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also strengthens your heart and improves circulation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking or swimming. If you’re unsure where to start, consider joining a local exercise class designed for seniors or working with a personal trainer who specializes in senior fitness.
By embracing these lifestyle changes, you can take significant strides toward better managing your blood pressure and enhancing your quality of life.
Medication Management for Senior Blood Pressure Crisis
| Metric | Description | Recommended Range/Value | Notes for Seniors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) | Pressure in arteries when heart beats | Less than 180 mm Hg during crisis | Above 180 mm Hg may indicate hypertensive crisis; seek immediate care |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) | Pressure in arteries when heart rests between beats | Less than 120 mm Hg during crisis | Above 120 mm Hg may indicate hypertensive crisis; urgent evaluation needed |
| Heart Rate | Number of heartbeats per minute | 60-100 bpm | Monitor for irregularities during crisis; tachycardia or bradycardia may complicate management |
| Symptoms to Monitor | Signs indicating blood pressure crisis | N/A | Severe headache, chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes, confusion |
| Time to Seek Emergency Care | Recommended response time after symptom onset | Within 1 hour | Delays increase risk of stroke, heart attack, or organ damage |
| Medication Adherence Rate | Percentage of prescribed doses taken | Above 90% | Critical for preventing crisis; seniors should follow regimen strictly |
| Follow-up Monitoring Frequency | Recommended frequency of blood pressure checks post-crisis | Weekly for first month | Ensures stabilization and adjustment of treatment |
For many seniors, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to manage high blood pressure effectively. In such cases, medication management becomes an essential part of your treatment plan. Various classes of antihypertensive medications are available, each designed to target different aspects of blood pressure regulation.
Your healthcare provider will work closely with you to determine the most appropriate medication based on your individual health profile and any other existing conditions. It’s crucial for you to understand the importance of adhering to prescribed medication regimens. Skipping doses or discontinuing medication without consulting your doctor can lead to dangerous spikes in blood pressure and increase the risk of complications.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will allow for ongoing assessment and adjustments to your medication as needed. By actively participating in your medication management plan, you can help ensure that you maintain optimal blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of serious health issues.
The Role of Diet in Managing High Blood Pressure in Seniors
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing high blood pressure among seniors like yourself. A well-balanced diet rich in whole foods can significantly impact your cardiovascular health. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is often recommended for individuals with high blood pressure; it emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while minimizing saturated fats and added sugars.
By adopting this dietary approach, you can provide your body with the nutrients it needs while effectively managing your blood pressure. In addition to following a specific dietary plan, it’s essential to stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption. Dehydration can lead to increased blood viscosity, which may elevate blood pressure levels.
On the other hand, excessive alcohol intake can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health. By making conscious choices about what you eat and drink, you can create a supportive environment for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels while enjoying delicious meals that nourish your body.
Exercise and Physical Activity Recommendations for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for seniors managing high blood pressure. Exercise not only helps lower blood pressure but also improves overall cardiovascular health and enhances quality of life. As you consider incorporating more movement into your routine, aim for a mix of aerobic exercises—such as walking, swimming, or cycling—and strength training activities that promote muscle health and stability.
It’s important to choose activities that you enjoy and feel comfortable doing. If you’re new to exercise or have existing health concerns, consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new fitness regimen. They may recommend working with a physical therapist or joining a senior fitness class tailored to your abilities.
By finding enjoyable ways to stay active, you’ll be more likely to stick with it long-term and reap the benefits of improved blood pressure management.
Stress Management Techniques for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Stress can significantly impact your blood pressure levels, making stress management techniques essential for seniors like yourself dealing with hypertension. Chronic stress triggers the release of hormones that can constrict blood vessels and elevate heart rate, leading to increased blood pressure over time. Therefore, finding effective ways to manage stress is crucial for maintaining optimal health.
Consider incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help calm your mind and reduce stress levels. Additionally, engaging in hobbies or spending time with loved ones can provide emotional support and serve as a healthy distraction from daily stressors.
By prioritizing stress management strategies, you create a more balanced lifestyle that supports both mental and physical well-being.
The Impact of High Blood Pressure on Senior Health
The consequences of high blood pressure extend far beyond elevated readings; they can profoundly affect various aspects of senior health. Chronic hypertension increases the risk of developing serious conditions such as heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and vision problems like hypertensive retinopathy. As you age, these risks become even more pronounced, making it imperative to take proactive measures in managing your blood pressure.
Moreover, high blood pressure can also impact cognitive function and mental health. Research has shown that individuals with untreated hypertension may experience cognitive decline or an increased risk of dementia over time. By understanding the far-reaching effects of high blood pressure on overall health, you are better equipped to prioritize management strategies that protect not only your cardiovascular system but also your cognitive well-being.
Support and Resources for Seniors Managing High Blood Pressure
Navigating the challenges of managing high blood pressure can feel overwhelming at times; however, numerous resources are available to support seniors like yourself on this journey. Local community centers often offer educational programs focused on hypertension management and healthy living tailored specifically for older adults. These programs provide valuable information while fostering connections with others facing similar challenges.
Additionally, online resources from reputable organizations such as the American Heart Association or the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute offer a wealth of information on managing high blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication adherence. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals who can guide you through this process and connect you with support groups or counseling services if needed. By leveraging these resources, you empower yourself with knowledge and support as you work toward better managing your blood pressure.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups and Follow-up Care for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Regular check-ups and follow-up care are vital components in managing high blood pressure effectively as a senior.
Consistent communication with your healthcare team ensures that any emerging issues are addressed promptly before they escalate into more significant concerns.
During these visits, take the opportunity to discuss any questions or concerns you may have regarding your treatment plan or lifestyle changes you’ve implemented. Open dialogue fosters a collaborative relationship between you and your healthcare provider, ultimately leading to better outcomes in managing high blood pressure. By prioritizing regular check-ups and follow-up care, you take an active role in safeguarding your health and enhancing your quality of life as you age gracefully.
Effective management of blood pressure is crucial for seniors, especially in times of crisis. For a comprehensive overview of strategies and tips tailored to older adults, you can refer to the article on senior health management. This resource provides valuable insights into maintaining optimal blood pressure levels and addressing potential health challenges. For more information, visit this article on senior health management.
FAQs
What is considered a blood pressure crisis in seniors?
A blood pressure crisis in seniors typically refers to a sudden and severe increase in blood pressure, often defined as a systolic pressure above 180 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure above 120 mm Hg. This condition requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
What are the common symptoms of a blood pressure crisis in elderly individuals?
Symptoms may include severe headache, chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes, confusion, nausea, and weakness. However, some seniors may not experience noticeable symptoms, making regular monitoring important.
How should a blood pressure crisis be managed in seniors?
Management involves immediate medical evaluation and treatment, which may include intravenous medications to lower blood pressure safely. It is critical to avoid rapid drops in blood pressure to prevent organ damage.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent blood pressure crises in seniors?
Yes, lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet low in sodium, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, and managing stress can help control blood pressure and reduce the risk of crises.
When should emergency services be contacted for a blood pressure crisis?
Emergency services should be contacted if a senior experiences symptoms like severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, sudden weakness or numbness, severe headache, or loss of consciousness, as these may indicate a hypertensive emergency.
Are blood pressure medications safe for seniors during a crisis?
Blood pressure medications are often necessary and can be safe when administered under medical supervision. Dosages and types of medication may be adjusted during a crisis to ensure effective and safe blood pressure reduction.
How often should seniors monitor their blood pressure to prevent crises?
Seniors should monitor their blood pressure regularly as advised by their healthcare provider, which may range from daily to weekly checks, especially if they have a history of hypertension or related health issues.
What role do healthcare providers play in managing blood pressure crises in seniors?
Healthcare providers assess the severity of the crisis, determine appropriate treatment, monitor for complications, and provide guidance on long-term blood pressure management to prevent future crises.