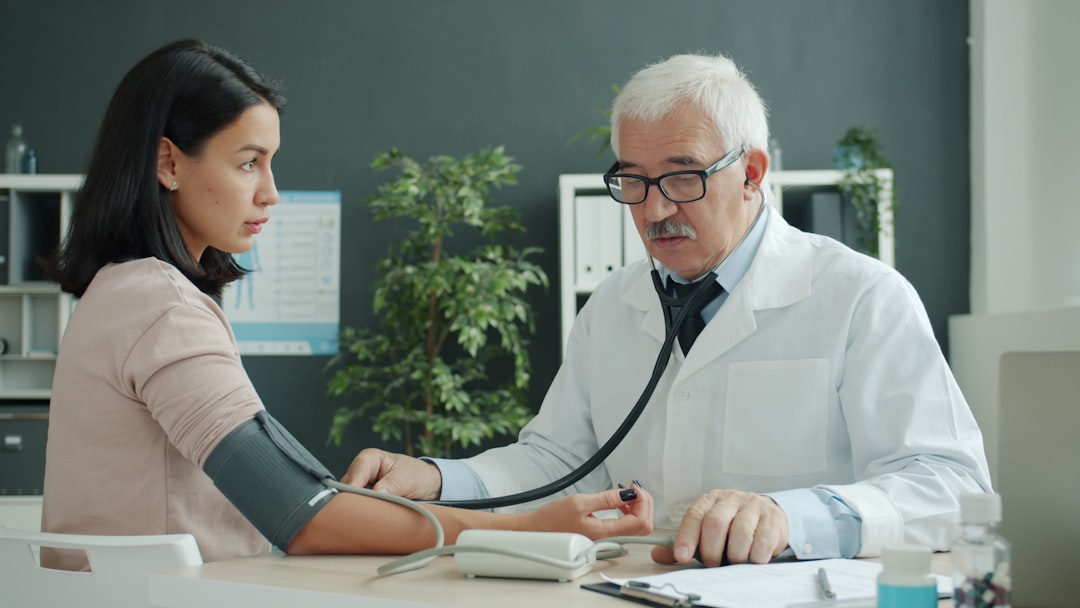
Medication Audits for Seniors: A Critical Healthcare Component
The importance of medication audits for seniors is significant in modern healthcare management. As the elderly population often relies on multiple prescriptions, systematic evaluation of their medications becomes essential. A medication audit examines whether each prescription is necessary, effective, and safe for the individual, helping to identify discrepancies and optimize treatment outcomes.
Regular audits can prevent adverse drug reactions and improve quality of life for older adults. Medication audits can uncover important patterns in prescription use. They may reveal potentially harmful drug interactions or identify medications that are no longer appropriate for a senior’s current health condition.
This preventive approach enables healthcare providers to intervene before problems develop, potentially reducing hospitalization rates and enhancing overall health outcomes. Medication audits represent a fundamental element of comprehensive geriatric care, with a focus on maintaining safety and ensuring treatment effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
- Regular medication audits are crucial to ensure the safety and effectiveness of senior health treatments.
- Mismanagement of medications in seniors can lead to serious health risks, including adverse drug interactions.
- Healthcare providers play a key role in monitoring and managing seniors’ medications to prevent complications.
- Polypharmacy, or the use of multiple medications, significantly increases the risk of negative health outcomes in seniors.
- Educating seniors and caregivers, along with using technology, enhances medication adherence and safety.
Understanding the Risks of Medication Mismanagement in Seniors
When you consider the risks associated with medication mismanagement in seniors, it becomes clear why vigilance is necessary. Seniors often face unique challenges, such as cognitive decline, physical limitations, and multiple chronic conditions, which can complicate their ability to manage medications effectively. Mismanagement can lead to serious consequences, including medication errors, increased hospital visits, and even life-threatening situations.
Understanding these risks is crucial for anyone involved in the care of older adults. Additionally, the consequences of medication mismanagement extend beyond physical health. Emotional and psychological well-being can also be affected when seniors experience adverse effects from their medications or when they struggle to adhere to complex regimens.
You may find that anxiety and depression can arise from the fear of taking the wrong medication or from the frustration of managing multiple prescriptions. By recognizing these risks, you can take proactive steps to mitigate them and ensure that seniors receive the care they deserve.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Senior Medication Management

As a healthcare provider, your role in senior medication management is pivotal. You are often the first line of defense against medication mismanagement, and your expertise can guide seniors and their caregivers through the complexities of their treatment plans. By conducting thorough assessments and maintaining open lines of communication, you can help ensure that seniors understand their medications and the importance of adherence.
Your involvement can make a significant difference in their health outcomes. Furthermore, collaboration among healthcare providers is essential in managing senior medications effectively. You may need to work closely with pharmacists, specialists, and primary care physicians to create a cohesive treatment plan that addresses all aspects of a senior’s health.
This multidisciplinary approach not only enhances the quality of care but also fosters an environment where seniors feel supported and empowered to take charge of their health. By being proactive and engaged in medication management, you can help seniors navigate their healthcare journey with confidence.
Common Medication-related Issues in Senior Health
In your experience with senior health, you may have encountered various medication-related issues that are particularly prevalent among older adults. One common issue is polypharmacy, where seniors take multiple medications simultaneously. This situation can lead to confusion about dosages and schedules, increasing the likelihood of missed doses or double dosing.
Additionally, some seniors may struggle with understanding the purpose of each medication, which can further complicate adherence. Another prevalent issue is the presence of inappropriate medications that may not be suitable for older adults due to their side effects or interactions with other drugs. For instance, certain medications may exacerbate cognitive decline or increase the risk of falls.
As you work with seniors, it’s essential to be aware of these common pitfalls and to advocate for regular reviews of their medication regimens. By addressing these issues head-on, you can help ensure that seniors receive safe and effective treatment tailored to their unique needs.
Conducting a Comprehensive Medication Audit for Seniors
| Metric | Description | Value | Unit | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Medications Reviewed | Total count of medications audited per patient | 8 | medications | Average per senior patient |
| Medication Errors Identified | Number of errors found during audit | 2 | errors | Includes dosage and timing errors |
| Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) | Incidents of ADRs reported | 1 | incident | Per 100 patients audited |
| Medication Adherence Rate | Percentage of patients following prescribed regimen | 85 | % | Based on patient self-reporting |
| Polypharmacy Prevalence | Percentage of patients taking 5 or more medications | 60 | % | Indicator of complex medication regimens |
| Potentially Inappropriate Medications (PIMs) | Number of PIMs identified per 100 patients | 15 | medications | Based on Beers Criteria |
| Medication Review Frequency | Average interval between medication reviews | 6 | months | Recommended review period |
When it comes to conducting a comprehensive medication audit for seniors, a systematic approach is key. Start by gathering all relevant information about the senior’s medical history, current medications, and any over-the-counter drugs or supplements they may be taking.
You should also engage with the senior and their caregivers to understand their perspectives on medication use and any challenges they face. Once you have compiled this information, analyze it critically to identify potential issues such as duplications, contraindications, or outdated prescriptions. It’s important to assess not only the medications themselves but also how they fit into the senior’s overall health plan.
After identifying any concerns, collaborate with other healthcare professionals to develop an action plan that addresses these issues effectively. A comprehensive medication audit is not just about identifying problems; it’s about creating solutions that enhance the quality of life for seniors.
Identifying Potential Drug Interactions and Adverse Reactions
As you delve deeper into senior medication management, one critical aspect to focus on is identifying potential drug interactions and adverse reactions. Given that many seniors take multiple medications simultaneously, the risk of interactions increases significantly. You should familiarize yourself with common drug interactions that could pose risks to older adults and remain vigilant in monitoring any new prescriptions or changes in dosage.
In addition to drug interactions, it’s essential to be aware of potential adverse reactions that may arise from medications. Seniors often have different physiological responses compared to younger adults due to age-related changes in metabolism and organ function. By closely monitoring seniors for signs of adverse reactions—such as dizziness, confusion, or gastrointestinal issues—you can intervene promptly and adjust their treatment plans as needed.
Your proactive approach can help prevent serious complications and ensure that seniors receive safe and effective care.
Strategies for Ensuring Safe and Effective Medication Use in Seniors
To ensure safe and effective medication use among seniors, you can implement several strategies that promote adherence and minimize risks. One effective approach is simplifying medication regimens whenever possible. This might involve consolidating medications or using combination therapies that reduce the number of pills a senior needs to take daily.
By streamlining their regimen, you can help alleviate confusion and improve adherence. Another strategy involves educating seniors about their medications in a way that is clear and understandable. You might consider using visual aids or written materials that outline each medication’s purpose, dosage instructions, and potential side effects.
Encouraging open communication between seniors and their healthcare providers fosters an environment where questions can be asked freely. By empowering seniors with knowledge about their medications, you can enhance their confidence in managing their health.
The Impact of Polypharmacy on Senior Health
Polypharmacy is a significant concern in senior health that warrants your attention as a caregiver or healthcare provider. The term refers to the concurrent use of multiple medications by a patient, often leading to increased risks of adverse effects and drug interactions. As you work with older adults who may be managing several chronic conditions, it’s crucial to recognize how polypharmacy can complicate their treatment plans and overall well-being.
The impact of polypharmacy extends beyond physical health; it can also affect cognitive function and quality of life. Seniors may experience confusion or memory issues as a result of taking numerous medications, which can further complicate adherence to their treatment regimens. By being aware of these challenges associated with polypharmacy, you can advocate for regular medication reviews and adjustments that prioritize safety while still addressing the senior’s health needs effectively.
Educating Seniors and Caregivers on Medication Management
Education plays a vital role in effective medication management for seniors and their caregivers. As someone involved in their care, you have the opportunity to provide valuable information that empowers them to take control of their health. Start by offering resources that explain the importance of adhering to prescribed regimens and understanding potential side effects or interactions associated with their medications.
These sessions could cover topics such as how to read prescription labels, the significance of keeping an updated medication list, and strategies for remembering doses. By fostering an environment of learning and support, you can help seniors feel more confident in managing their medications effectively.
Implementing Technology and Tools for Medication Management in Seniors
In today’s digital age, technology offers innovative solutions for improving medication management among seniors. You might explore various tools such as mobile apps designed specifically for tracking medications and sending reminders for doses. These applications can simplify the process for both seniors and caregivers by providing timely notifications about when to take each medication.
Moreover, telehealth services have become increasingly popular as a means for seniors to consult with healthcare providers without needing to travel physically. This convenience allows for regular check-ins regarding medication management while ensuring that any concerns are addressed promptly. By embracing technology as part of your approach to senior care, you can enhance communication and streamline medication management processes.
Monitoring and Evaluating the Effectiveness of Senior Medication Management
Finally, monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of senior medication management is essential for ensuring optimal health outcomes. Regular follow-ups allow you to assess how well seniors are adhering to their prescribed regimens and whether any adjustments are necessary based on their evolving health status. You should encourage open dialogue during these evaluations so that seniors feel comfortable discussing any challenges they face.
Additionally, consider implementing metrics or benchmarks to measure the success of your medication management strategies over time. This could involve tracking hospital readmission rates or improvements in specific health markers related to chronic conditions being treated with medications. By continuously monitoring these factors, you can refine your approach to senior care and ensure that each individual receives personalized treatment tailored to their unique needs.
In conclusion, effective senior health medication management requires a multifaceted approach involving audits, education, collaboration among healthcare providers, and ongoing monitoring. By prioritizing these elements in your practice or caregiving role, you can significantly enhance the quality of life for seniors while minimizing risks associated with medication mismanagement.
A recent article on senior health medication audits highlights the importance of regularly reviewing medications to ensure their effectiveness and safety for older adults. This process can help identify potential drug interactions and reduce the risk of adverse effects. For more information on this topic, you can read the article on senior health at Explore Senior Health.
WATCH THIS WARNING: 💊 NSAID Kidney Damage: The Hidden Danger Seniors Don’t Know About
FAQs
What is a senior health medication audit?
A senior health medication audit is a systematic review of the medications taken by older adults. It aims to ensure that all prescribed drugs are appropriate, effective, and safe, minimizing the risk of adverse effects and drug interactions.
Why is a medication audit important for seniors?
Medication audits help identify potential issues such as duplicate therapies, incorrect dosages, or harmful drug interactions. Since seniors often take multiple medications, audits are crucial to optimize treatment and improve overall health outcomes.
Who conducts a senior health medication audit?
Medication audits are typically conducted by healthcare professionals such as pharmacists, physicians, or nurses who specialize in geriatric care. They review medical records, prescriptions, and sometimes consult with the patient and caregivers.
How often should seniors have a medication audit?
It is recommended that seniors undergo a medication audit at least once a year or whenever there is a significant change in their health status or medication regimen.
What information is reviewed during a medication audit?
The audit reviews all current medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, supplements, and herbal products. It also considers the patient’s medical history, allergies, and any side effects experienced.
Can a medication audit reduce hospitalizations for seniors?
Yes, by identifying and addressing medication-related problems early, audits can reduce the risk of adverse drug events, which are a common cause of hospital admissions among seniors.
What should seniors do to prepare for a medication audit?
Seniors should bring a complete list of all medications they are taking, including dosages and frequency. They should also be ready to discuss any side effects or concerns with their healthcare provider.
Are medication audits covered by insurance?
Coverage varies depending on the healthcare system and insurance plan. Some plans may cover medication reviews as part of routine care, especially for seniors with chronic conditions.
What happens after a medication audit?
After the audit, healthcare providers may adjust medication types, dosages, or schedules. They may also provide education on proper medication use and monitor the patient for improvements or side effects.
Can medication audits help prevent medication errors?
Yes, medication audits are an effective tool to detect and prevent errors such as incorrect dosing, harmful drug interactions, and unnecessary medications, thereby enhancing patient safety.
