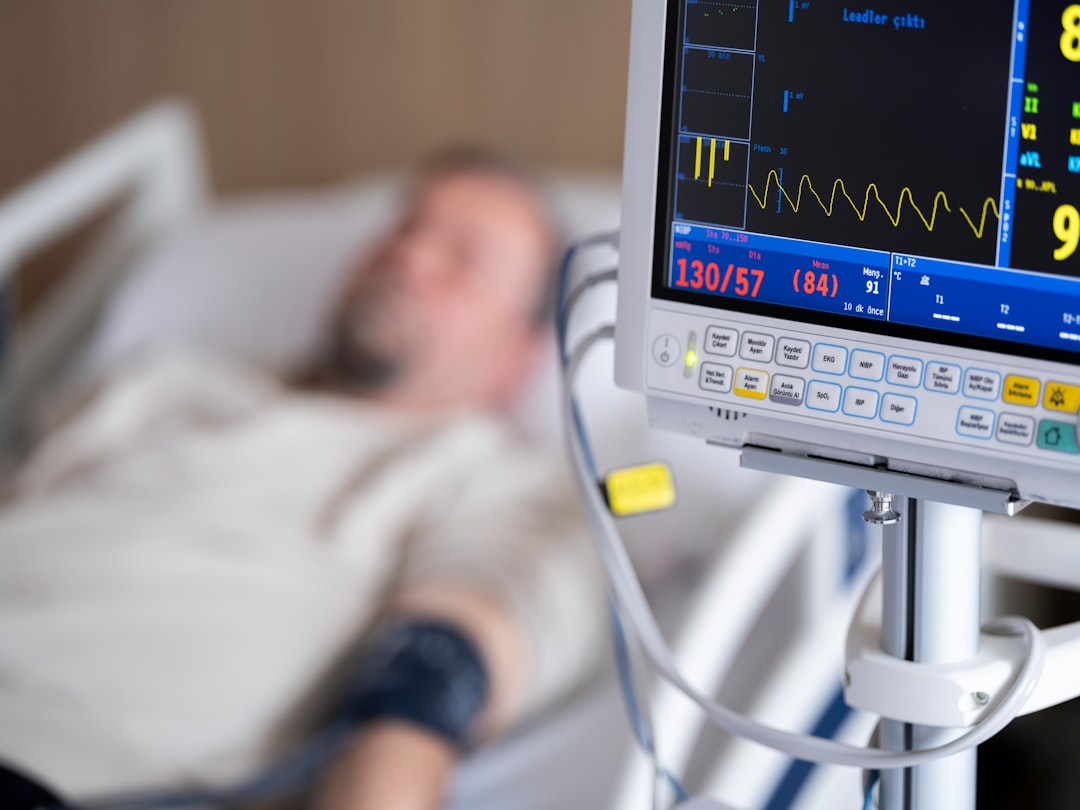
As individuals age, the cardiovascular system undergoes significant changes, with blood pressure fluctuations becoming a critical health concern. Blood pressure, which measures the force exerted by blood against arterial walls, can be influenced by multiple factors including lifestyle habits, dietary choices, and existing health conditions.
This acute condition can precipitate severe health complications including myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accidents, and renal failure. For seniors, understanding the nature and implications of a blood pressure crisis is essential for preventive health management. The probability of experiencing a blood pressure crisis increases with advancing age, particularly in individuals with comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus or cardiovascular disease.
Pharmaceutical agents and lifestyle factors may further contribute to hypertensive episodes. It is important to note that a blood pressure crisis represents more than a transient elevation; it often indicates underlying pathophysiological processes requiring prompt medical evaluation. Knowledge of hypertension risk factors and potential complications enables seniors to participate actively in their healthcare decisions and implement appropriate preventive strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Blood pressure crises in seniors require prompt recognition of symptoms and immediate action to prevent complications.
- Proper medication management and adherence are crucial for controlling high blood pressure in older adults.
- Lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management, play a significant role in managing blood pressure effectively.
- Regular home monitoring of blood pressure helps seniors and caregivers track health status and detect issues early.
- Seeking timely medical help and following long-term management strategies are essential for preventing recurrent blood pressure crises.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Blood Pressure Crisis
Recognizing the symptoms of a blood pressure crisis is vital for timely intervention. You may experience a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity. Common signs include severe headaches, shortness of breath, chest pain, and visual disturbances.
You might also feel dizzy or lightheaded, which can be alarming. These symptoms are your body’s way of signaling that something is wrong, and ignoring them could lead to serious health consequences. In some cases, you may not experience any noticeable symptoms at all, which is why regular monitoring of your blood pressure is essential.
If you have a history of hypertension or other cardiovascular issues, being vigilant about any changes in your health is crucial. If you notice any combination of these symptoms or if your blood pressure readings are consistently high, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Early recognition can make a significant difference in the outcome of a blood pressure crisis.
Immediate Steps to Take in a Blood Pressure Crisis
If you find yourself in a situation where you suspect a blood pressure crisis, taking immediate action is critical. First and foremost, remain calm. Stress can exacerbate high blood pressure, so try to find a quiet space where you can sit down and breathe deeply.
If you have a blood pressure monitor at home, check your readings to confirm whether they are indeed at crisis levels. If they are, do not hesitate to call for help or have someone take you to the nearest emergency room. While waiting for medical assistance, it’s advisable to avoid any strenuous activity or stressors that could further elevate your blood pressure.
If you have prescribed medications for hypertension, take them as directed unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional. Staying hydrated can also be beneficial; however, be cautious with fluid intake if you have been advised to limit it due to other health conditions. Remember that acting quickly can significantly impact your health outcomes during a blood pressure crisis.
Medication Management for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Managing high blood pressure often involves medication, especially for seniors who may have multiple health concerns. Your healthcare provider may prescribe various antihypertensive medications tailored to your specific needs. These can include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, among others.
It’s essential to understand how each medication works and its potential side effects so that you can communicate effectively with your doctor about any concerns. Adhering to your medication regimen is crucial for managing high blood pressure effectively. You might find it helpful to set reminders or use pill organizers to ensure you take your medications as prescribed.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will allow for adjustments in your treatment plan if necessary. Additionally, be open about any side effects you experience; there may be alternative medications or dosages that could work better for you.
Lifestyle Changes to Help Manage Blood Pressure in Seniors
| Metric | Description | Recommended Range/Value | Notes for Seniors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) | Pressure in arteries when heart beats | Less than 180 mm Hg during crisis | Values above 180 require immediate medical attention |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) | Pressure in arteries when heart rests between beats | Less than 120 mm Hg during crisis | Values above 120 indicate hypertensive crisis |
| Heart Rate | Number of heartbeats per minute | 60-100 bpm normal; monitor for irregularities | Irregular or very high rates require urgent care |
| Symptoms to Monitor | Signs indicating hypertensive emergency | Severe headache, chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes | Presence of symptoms necessitates emergency response |
| Response Time | Time to seek medical help after crisis onset | Within 1 hour | Faster response reduces risk of complications |
| Medication Adherence | Percentage of prescribed doses taken | Above 90% | Critical to prevent crisis recurrence |
| Follow-up Frequency | Regular check-ups post-crisis | Every 1-3 months | Ensures blood pressure control and medication adjustment |
In addition to medication, making lifestyle changes can significantly impact your blood pressure management. You might consider adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium intake. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is particularly effective for lowering blood pressure and can be an excellent guideline for you to follow.
Physical activity is another critical component of managing high blood pressure. Engaging in regular exercise can help strengthen your heart and improve circulation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking or swimming.
However, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program to ensure it’s safe for you based on your current health status.
Monitoring Blood Pressure at Home for Seniors
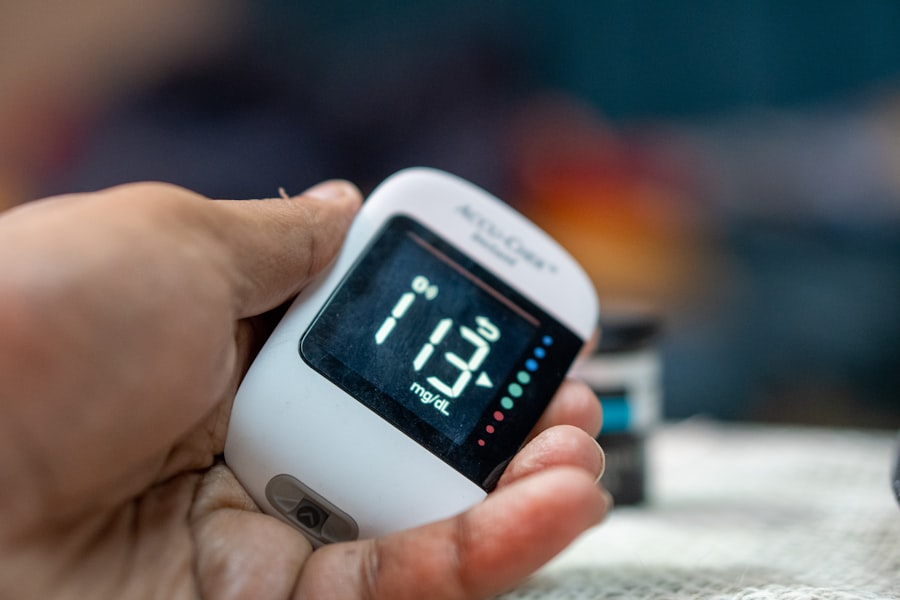

Monitoring your blood pressure at home is an effective way to keep track of your cardiovascular health. By regularly checking your readings, you can identify trends and make necessary adjustments in consultation with your healthcare provider. Home blood pressure monitors are widely available and easy to use; however, it’s essential to choose one that is validated for accuracy.
When measuring your blood pressure at home, ensure that you follow the instructions carefully for the most accurate results. Sit quietly for a few minutes before taking a reading and avoid caffeine or smoking beforehand. Keeping a log of your readings can also be beneficial when discussing your health with your doctor.
This proactive approach empowers you to take charge of your health and make informed decisions regarding your treatment plan.
The Role of Diet in Managing Blood Pressure Crisis in Seniors
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing blood pressure levels effectively. As a senior, focusing on nutrient-dense foods can help you maintain optimal health while keeping hypertension at bay. Incorporating foods rich in potassium—such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach—can counteract the effects of sodium and help lower blood pressure.
Additionally, reducing processed foods that are high in salt and sugar is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Instead of reaching for snacks laden with preservatives and unhealthy fats, opt for whole foods that nourish your body. Experimenting with herbs and spices instead of salt can enhance flavor without compromising your health goals.
By making conscious dietary choices, you can significantly impact your overall well-being and reduce the risk of experiencing a blood pressure crisis.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to manage high blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health. As a senior, engaging in moderate exercise not only helps lower blood pressure but also enhances mobility and reduces the risk of falls—a common concern among older adults. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be enjoyable ways to stay active while reaping the benefits of exercise.
It’s essential to find an exercise routine that suits your abilities and preferences. Consider joining a local fitness class designed for seniors or working with a personal trainer who specializes in senior fitness. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program to ensure it aligns with your health status and capabilities.
By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, you can take significant strides toward managing high blood pressure effectively.
Stress Management Techniques for Seniors with High Blood Pressure
Stress can be a significant contributor to elevated blood pressure levels, making stress management techniques essential for seniors dealing with hypertension. You might find practices such as mindfulness meditation or deep-breathing exercises beneficial in reducing stress and promoting relaxation. Setting aside time each day for these activities can help create a sense of calm amidst life’s challenges.
Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring you joy can also serve as an effective stress reliever. Whether it’s gardening, painting, or spending time with loved ones, finding outlets for relaxation is crucial for maintaining emotional well-being. Additionally, consider seeking support from friends or family members who understand what you’re going through; sharing experiences can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
Seeking Medical Help for Blood Pressure Crisis in Seniors
When faced with a blood pressure crisis, seeking medical help promptly is paramount. If you experience symptoms such as severe headaches or chest pain alongside high blood pressure readings, don’t hesitate to call emergency services or visit the nearest hospital. Your health should always be your top priority.
Even if symptoms seem manageable at first glance, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your condition thoroughly. They may perform tests to determine the underlying cause of the crisis and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs. Remember that timely intervention can prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Long-Term Strategies for Managing Blood Pressure Crisis in Seniors
Managing high blood pressure is not just about addressing immediate crises; it requires long-term strategies that promote overall cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your condition and making necessary adjustments to your treatment plan over time. Incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine will also contribute significantly to long-term management of high blood pressure.
This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, and adhering to prescribed medications diligently. By taking these proactive steps and remaining vigilant about your health, you empower yourself to lead a fulfilling life while minimizing the risks associated with high blood pressure crises. In conclusion, understanding the complexities surrounding blood pressure crises in seniors is vital for maintaining optimal health as you age.
By recognizing symptoms early on and taking immediate action when necessary, along with implementing lifestyle changes and medication management strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing severe complications related to hypertension. Your commitment to monitoring your health and making informed choices will ultimately lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life.
Effective management of blood pressure is crucial for seniors, especially in times of crisis.